Tables in SQL consists of columns and rows, resembling an excel spreadsheet. These tables are contained in a database. The first thing we want to do when we are creating a database is to define our database schema by creating all the different tables. Once all the tables are created, we can start inserting data into each table.
In order to create a table, we start off by assigning a name. Then we would need to define each column (which is an attribute) and also indicate their data types.
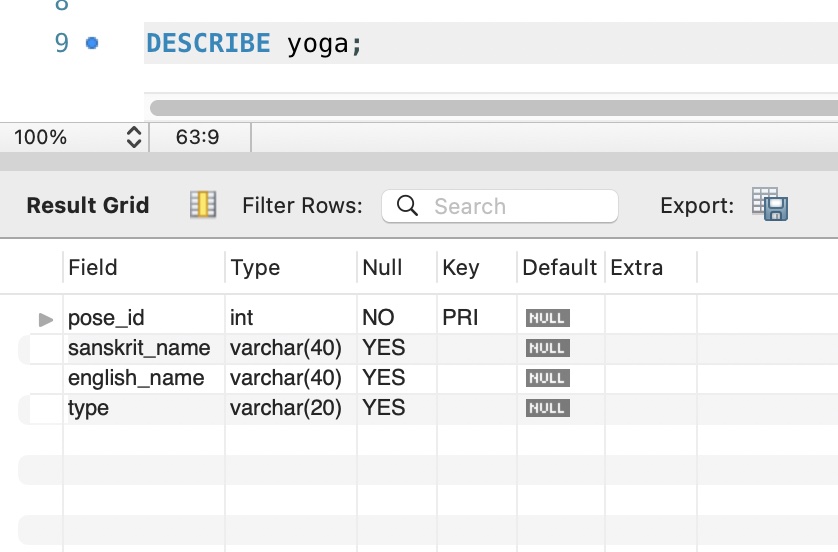
In the below example, our table name is yoga. Our attributes (column names) are: pose_id, sanskrit_name, english_name, and type. Next to each attribute is the data type. So, for pose_id, the data type is INT (which means it is a whole number) and it is also set to be the PRIMARY KEY.

Alternatively, we can define the primary key in the format of the example below:

Once the table is created and we want to view its structure, we can do so using the DESCRIBE command:
In order to delete the table, we can do so by executing the below statement:
DROP TABLE yoga;Let’s say we want to alter the table by adding another column called cue. We can do so with the below statement, indicating the name of the column and defining its data type:
ALTER TABLE yoga
ADD cue VARCHAR(100);If we wanted to rename the column cue to main_cue, we can execute the statement below:
ALTER TABLE yoga
RENAME COLUMN cue
TO main_cue;Now, if we decided to delete this newly renamed column, main_cue, we can drop the column by running the line below:
ALTER TABLE yoga
DROP COLUMN main_cue;Here’s a video to review the examples mentioned:
We can also reorder the columns within our table. We would choose which column we want to move and then indicate which column to place it after:
ALTER TABLE yoga
MODIFY main_cue VARCHAR(100)
AFTER english_name;Here is a video to go over an example of reordering columns:

